Regular sleep timing is a crucial factor in cardiovascular health, surpassing even the commonly emphasised sleep duration in importance. Research shows that maintaining regular sleep timing helps protect against heart disease and related conditions.
This groundbreaking insight is derived from a study titled “Sleep regularity and major adverse cardiovascular events: a device-based prospective study in 72 269 UK adults“, which challenges our conventional understanding of sleep’s impact on heart health.
Cardiovascular diseases claim over 17 million lives globally each year, with more than 7 million deaths from coronary heart disease and 6 million from stroke. While the medical community has long focused on sleep duration, evidence suggests that the consistency of our sleep schedule might play an even more vital role in preventing these conditions.
The relationship between sleep patterns and heart health affects multiple body systems. When sleep timing varies, it creates a series of changes in the body, including disrupted hormone levels, increased inflammation, and altered metabolism (the body’s process of converting food into energy). These disruptions cause tiredness and increase health risks.
Studies demonstrate that maintaining consistent sleep patterns is crucial for health. Inconsistent sleep patterns can negatively affect blood pressure regulation and immune function, underscoring the importance of regular sleep timing for overall health.
This post examines key sleep regularity and heart health findings, exploring how consistent sleep schedules influence cardiovascular risk. We’ll analyse the science behind these connections, examine common assumptions about sleep duration, and uncover why timing might matter more than hours spent asleep.
Research Findings That Changed Sleep Understanding on Irregular Sleep
Our understanding of sleep’s role in heart health has undergone a significant evolution. While scientists traditionally focused on sleep duration, a paradigm shift occurred when researchers identified the greater importance of timing consistency in maintaining cardiovascular health.
A pioneering investigation on sleep regularity and its adverse effect on cardiovascular set out to challenge conventional wisdom about sleep patterns. The scientists employed advanced wrist-worn technology to track sleep behaviours, calculating unique Sleep Regularity Index (SRI) scores that measured how consistently participants maintained their sleep schedules.
The investigation revealed striking patterns in regular sleep timing. Those with highly irregular sleep faced a 26% higher risk of cardiovascular events compared to consistent sleepers. Perhaps most telling, achieving recommended sleep hours offered no protection against these risks when sleep timing varied significantly.
Through detailed analysis, the research team discovered that improving sleep consistency yielded measurable benefits. Every incremental increase in regularity score corresponded with better cardiovascular outcomes. A particularly notable finding showed that reaching an SRI of 77.1 reduced cardiovascular event risk by 15%.
The implications proved especially significant for those with moderate sleep irregularity. These individuals showed an 8% higher risk of cardiovascular events, yet importantly, maintaining recommended sleep duration helped offset their risks. However, this protective effect vanished in those with highly irregular patterns.
These discoveries signal a fundamental shift in how we view sleep’s relationship with heart health. While sleep duration maintains importance, the evidence suggests that consistency in our daily sleep schedule plays an equally, if not more vital, role in cardiovascular protection. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions about our sleep habits.
Regular Sleep Timing Facts that Matter
The human body operates on intricate biological rhythms that influence every aspect of health. When regular sleep timing aligns with these natural patterns, it creates optimal conditions for cardiovascular function. This synchronisation affects everything from blood pressure regulation to cellular repair mechanisms.
Consistent sleep schedules strengthen the heart’s natural rhythm. Studies examining cardiovascular health show that individuals maintaining stable sleep patterns experience a 33% lower risk of heart disease mortality than those with variable schedules. The protective effects translate through improved blood pressure control and enhanced vascular function.
Sleep consistency influences fundamental metabolic processes. Research reveals that disrupting regular sleep timing for just six nights can trigger pre-diabetic blood sugar levels in healthy adults. These metabolic changes occur before noticeable effects on weight or appetite become apparent.
Global health data paints a compelling picture of sleep’s cardiovascular impact. The World Health Organisation reports that cardiovascular diseases claim 17 million lives annually, with irregular sleep patterns contributing significantly to this burden. Evidence suggests that improving sleep consistency could prevent millions of premature deaths.
The body’s stress response system shows particular sensitivity to sleep timing. When sleep patterns vary, cortisol levels become dysregulated, increasing inflammation throughout the cardiovascular system. This inflammatory response damages blood vessels and accelerates the development of heart disease.
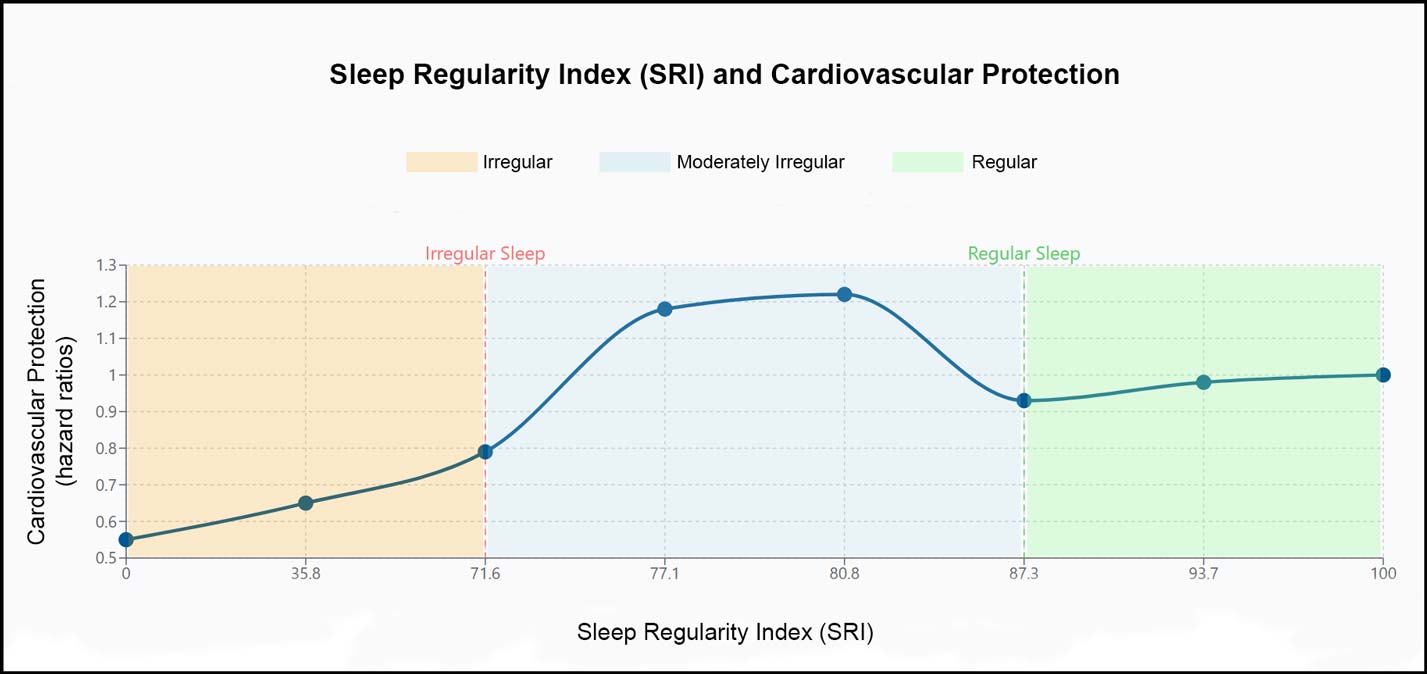
Understanding Sleep Regularity Index and Heart Health
Sleep measurement has evolved beyond simple duration tracking. Scientists developed the Sleep Regularity Index (SRI), scoring sleep patterns from 0 to 100. Higher scores indicate more excellent stability in daily sleep-wake cycles, providing valuable insights into cardiovascular protection.
The UK Biobank study revealed compelling connections between SRI scores and heart health. Participants scoring above 87.3 showed notable cardiovascular resilience. Meanwhile, those scoring below 71.6 faced substantially higher risks of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Measuring sleep consistency through SRI captures subtle variations in sleep behaviour. The index accounts for bedtime fluctuations, wake-up times, and night-time disturbances. This comprehensive approach to regular sleep timing provides a more profound understanding than traditional sleep diaries.
Analysis of SRI patterns highlighted critical thresholds. The data showed that achieving an SRI score above 80 corresponded with an 18% reduction in cardiovascular events. This finding establishes clear targets for regular sleep-timing interventions in clinical practice.
The relationship between SRI scores and heart health follows a near-linear pattern. Every incremental improvement in sleep regularity yields measurable cardiovascular benefits. This progressive relationship suggests that even minor improvements in consistency can enhance heart protection.
Regular Sleep Timing Versus Sleep Duration
Irregular sleep affects the heart through multiple biological mechanisms. The human circadian system coordinates cardiovascular processes throughout the day. When regular sleep timing falters, this orchestration disrupts blood pressure control and heart rhythm.
Molecular studies reveal how sleep inconsistency impacts heart cells. Variable sleep patterns alter gene expression in cardiovascular tissues, affecting over 700 genes involved in heart function. These changes influence regular sleep timing responses and vascular health.
Night-time blood pressure decreases typically during sleep, a phenomenon called “nocturnal dipping.” Sleep irregularity disrupts this protective mechanism. Studies show that individuals with inconsistent sleep schedules often lose this natural blood pressure reduction, increasing strain on their hearts.
The body’s inflammatory responses show particular sensitivity to sleep patterns. Irregular sleep triggers increased production of inflammatory proteins, creating an environment that accelerates arterial damage. This inflammation contributes to premature cardiovascular ageing.
Sleep pattern variability affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate and blood vessel function. Research demonstrates that irregular sleepers experience reduced heart rate variability, a marker associated with increased cardiovascular risk.
The Science Behind Irregular Sleep and Heart Disease
Standard sleep guidelines emphasise getting seven to nine hours nightly. However, the UK Biobank study challenges this singular focus, showing that regular sleep timing creates distinct cardiovascular benefits independent of duration.
Meeting sleep duration recommendations alone provided insufficient protection for irregular sleepers. The data revealed that participants with irregular patterns faced elevated cardiovascular risks even when achieving recommended sleep hours. This finding reshapes our perspective on regular sleep timing as a crucial health factor.
The relationship between sleep duration and heart health varies based on consistency patterns. Participants with moderate sleep irregularity who met duration guidelines showed improved outcomes. However, those with highly irregular sleep gained no protective benefits from longer sleep duration.
Clinical observations support these findings across different age groups. Adults maintaining consistent sleep schedules displayed better cardiovascular markers regardless of total sleep time. The evidence suggests regularity might be a stronger predictor of heart health than duration alone.
The distinction becomes particularly relevant for shift workers and individuals with variable schedules. Research indicates that consistent sleep timing within their constraints provides more excellent cardiovascular protection than focusing solely on accumulating sufficient hours.

Practical Steps to Maintain Consistent Sleep Patterns
Establishing regular sleep timing begins with understanding personal circadian rhythms. The body’s internal clock responds best to consistency, creating a foundation for cardiovascular health. Minor adjustments in daily routines can significantly impact sleep regularity.
Environmental factors play crucial roles in maintaining sleep consistency. Exposure to natural light during morning hours helps anchor regular sleep timing. Creating darkness in the evening supports the body’s natural melatonin production, facilitating consistent sleep onset.
Sleep quality improves through structured evening routines. Research shows that maintaining consistent pre-sleep activities helps signal the body to prepare for rest. This preparation enhances the likelihood of maintaining regular sleep patterns.
Technology use significantly influences sleep consistency. Studies reveal that blue light exposure from devices disrupts natural sleep timing. Implementing technology boundaries in evening hours helps preserve established sleep schedules.
Exercise timing affects sleep regularity patterns. Morning or early afternoon physical activity supports consistent sleep-wake cycles. This alignment of activity with natural circadian rhythms enhances overall sleep consistency.
The UK Biobank study’s findings emphasise sleep consistency’s vital role in cardiovascular health. Their data reveals that minor improvements in sleep regularity yield measurable benefits for heart health. Each step toward more consistent sleep patterns contributes to cardiovascular protection.
This evidence reshapes our approach to sleep health. While duration maintains importance, consistency emerges as a powerful tool for cardiovascular protection. The science points clearly to sleep timing’s fundamental role in maintaining heart health across the lifespan.
Sources
- Bechtold, Dawn A., Loudon, Andrew S.I. Hypothalamic clocks and rhythms in feeding behaviour. Trends in Neurosciences, 36(2), 74-82, 2013.
- Broussard, Josiane L., Ehrmann, David A., Van Cauter, Eve, Tasali, Esra, Brady, Matthew J. Impaired insulin signaling in human adipocytes after experimental sleep restriction: a randomised, crossover study. Annals of Internal Medicine, 157(8), 549-557, 2012.
- Buxton, Orfeu M., Pavlova, Milena, Reid, Emily W., Wang, Wei, Simonson, Donald C., Adler, Gail K. Sleep restriction for 1 week reduces insulin sensitivity in healthy men. Diabetes, 59(9), 2126-2133, 2010.
- Cappuccio FP, Cooper D, D’Elia L, Strazzullo P, Miller MA. Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur Heart J. 2011 Jun;32(12):1484-92.
- Chaput, Jean-Philippe & Biswas, Raaj & Ahmadi, Matthew & Cistulli, Peter & Rajaratnam, Shantha & Bian, Wenxin & St-Onge, Marie-Pierre & Stamatakis, Emmanuel. (2024). Sleep regularity and major adverse cardiovascular events: a device-based prospective study in 72 269 UK adults. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. jech-2024.
- Cribb L, Sha R, Yiallourou S, Grima NA, Cavuoto M, Baril AA, Pase MP. Sleep regularity and mortality: a prospective analysis in the UK Biobank. Elife. 2023 Nov 23;12:RP88359.
- Dibner, Charna, Schibler, Ueli, Albrecht, Urs. The mammalian circadian timing system: organisation and coordination of central and peripheral clocks. Annual Review of Physiology, 72, 517-549, 2010.
- Fischer, Dorothee, Klerman, Elizabeth B., Phillips, Andrew J.K. Measuring sleep regularity: theoretical properties and practical usage of existing metrics. Sleep, 44(5), zsab103, 2021.
- Forrestel, Alexander C., Miedlich, Susanne U., Yurcheshen, Michael, Wittlin, Steven D., Sellix, Michael T. Chronomedicine and type 2 diabetes: shining some light on melatonin. Diabetologia, 60(5), 808-822, 2017.
- Gabriel, Bruno M., Zierath, Juleen R. Circadian rhythms and exercise – re-setting the clock in metabolic disease. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 15(4), 197-206, 2019.
- Garfinkel, Doron, Zorin, Michael, Wainstein, Julio, Matas, Zipora, Laudon, Moshe, Zisapel, Nava. Efficacy and safety of prolonged-release melatonin in insomnia patients with diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, crossover study. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy, 4, 307-313, 2011.
- Heinzer, Raphael C., Stanchina, Michael L., Malhotra, Atul, Fogel, Robert B., Patel, Sanjay R., Jordan, Amy S., et al. Lung volume and continuous positive airway pressure requirements in obstructive sleep apnea. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 172(1), 114-117, 2005.
- Li, Yanping, Vgontzas, Alexandros N., Fernandez-Mendoza, Julio, Bixler, Edward O., Sun, Yingting, Zhou, Junying, et al. Insomnia with physiological hyperarousal is associated with hypertension. Hypertension, 65(3), 644-650, 2015.
- Li, Yanping, Zhang, Xiang, Winkelman, John W., Redline, Susan, Hu, Frank B., Stampfer, Meir. Association between insomnia symptoms and mortality: a prospective study of U.S. men. Circulation, 129(7), 737-746, 2014.
- Luchetti, Francesca, Canonico, Barbara, Betti, Michele, Arcangeletti, Maria, Pilolli, Francesca, Piroddi, Marta, et al. Melatonin signaling and cell protection function. The FASEB Journal, 24(10), 3603-3624, 2010.
- Martinez-Garcia, Miguel A., Campos-Rodriguez, Francisco, Catalán-Serra, Pablo, Soler-Cataluña, Juan-José, Almeida-Gonzalez, Carmen, De la Cruz Morón, Ignacio. Cardiovascular mortality in obstructive sleep apnea in the elderly: role of long-term continuous positive airway pressure treatment. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 186(9), 909-916, 2012.
- Meng, Lina, Zheng, Yang, Hui, Rutai. The relationship of sleep duration and insomnia to risk of hypertension incidence: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Hypertension Research, 36(11), 985-995, 2013.
- Phillips, Andrew J.K., Clerx, William M., O’Brien, Conor S., Sano, Akane, Barger, Laura K., Picard, Rosalind W., Lockley, Steven W., Klerman, Elizabeth B., Czeisler, Charles A. Irregular sleep/wake patterns are associated with poorer academic performance and delayed circadian and sleep/wake timing. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 3216, 2017.
- Ross, Robert, Chaput, Jean-Philippe, Giangregorio, Lora M., Janssen, Ian, Saunders, Travis J., Kho, Michelle E., et al. Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Adults aged 18-64 years and Adults aged 65 years or older. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 45(10), S57-S102, 2020.
- Sletten TL, Weaver MD, Foster RG, Gozal D, Klerman EB, Rajaratnam SMW, Roenneberg T, Takahashi JS, Turek FW, Vitiello MV, Young MW, Czeisler CA. The importance of sleep regularity: a consensus statement of the National Sleep Foundation sleep timing and variability panel. Sleep Health. 2023 Dec;9(6):801-820.
- Van Dongen HP, Maislin G, Mullington JM, Dinges DF. The cumulative cost of additional wakefulness: dose-response effects on neurobehavioral functions and sleep physiology from chronic sleep restriction and total sleep deprivation. Sleep. 2003 Mar 15;26(2):117-26.
- van Hees, Vincent T., Sabia, Séverine, Jones, Samuel E., Wood, Andrew R., Anderson, Karina N., Kivimäki, Mika, et al. Estimating sleep parameters using an accelerometer without sleep diary. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 12975, 2018.
- Vaughn, Bradley V., D’Cruz, O’Neill F. Cardinal manifestations of sleep disorders. In: Kryger, Meir H., Roth, Thomas, Dement, William C., editors. Principles and practice of sleep medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2016.
- Watson, Nathaniel F., Badr, M. Safwan, Belenky, Gregory, Bliwise, Donald L., Buxton, Orfeu M., Buysse, Daniel. Recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: a joint consensus statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep, 38(6), 843-844, 2015.
- Windred, Daniel P., Burns, Alexander C., Lane, Jacqueline M., Clerx, William M., Phillips, Andrew J.K. Sleep regularity is a stronger predictor of mortality risk than sleep duration: a prospective cohort study. Sleep, 47(3), 2024.
- Windred DP, Jones SE, Russell A, Burns AC, Chan P, Weedon MN, Rutter MK, Olivier P, Vetter C, Saxena R, Lane JM, Cain SW, Phillips AJK. Objective assessment of sleep regularity in 60 000 UK Biobank participants using an open-source package. Sleep. 2021 Dec 10;44(12):zsab254.
- World Health Organization. Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013-2020. Geneva: WHO Press, 2013.
- World Heart Federation. World congress of cardiology & cardiovascular health 2016. And ‘What is cardiovascular disease?’.
- Zhang, Yong, Papantoniou, Kyriaki. Night shift work and its carcinogenicity. The Lancet Oncology, 20(10), e550, 2019.


